With the continued push to cloud and the need for devices to be mobile, Microsoft Entra ID, formally AzureAD, plays a key role in user access management. With devices being remote and off the corporate network, the need to manage local administrative user accounts can be cumbersome. Today, we take a deep dive into how you can manage local administrative accounts using Microsoft Entra ID and Windows LAPS.
What is Microsoft Entra ID?
Microsoft Entra ID is Microsoft’s cloud identity management platform. Modeled after traditional Active Directory, Entra ID allows administrator to control users and access from a central location. We like to think of Entra ID as Active Directory, but in the cloud and available anywhere in the world. There are many core differences between the two offers, but those will be discussed in a later post.
What is Windows LAPS?
Windows LAPS is a Windows local administrator password management tool. The tool allows computers bound to an Active Directory or Entra ID to automatically set, store and rotate local administrator accounts based on policy. Passwords can be retrieved in either Active Directory or Entra ID.
What is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is a device management platform that allows administrators to manage and control remote devices. This control and management is to ensure compliance and safety of company data and property. We like to think of Microsoft Intune as the cloud’s version of Group Policy.
Setup Windows LAPS with Entra ID
Microsoft Entra ID is pre-configured to work with Windows LAPS. The only requirement is you must have an active Microsoft Entra ID environment. Entra ID comes default when you setup either a Microsoft 365 tenant or Azure tenant.
First, the workstation must be bound to the Entra ID environment. By default, this can be done by any user in the Entra ID. It is recommended to adjust this setting to ensure only the proper personnel can add machines to Entra ID. Navigate to Settings -> Accounts. On the Accounts page, click the Access work or school option.

Once connected to Entra ID, you should see the device in the Entra ID Admin Center. Expand Devices -> All devices to ensure the newly added device is enabled.

At this point, the workstation is connected and communicating with Entra ID. If your organization has one of the Intune includes plans, Microsoft Intune can be used to automate the following steps. This tutorial will configure settings manually without the use of Intune.
Open local group policy by navigating to Start -> Edit group policy. The group policy window will open. From there, navigate to the Windows LAPS local group police settings at Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> LAPS. Update the following objects:
- Configure password backup directory: Should be enabled with the backup directory set to Azure Active Directory. This tells the workstation to report back to Entra ID that current administrative password.
- Name of administrator account to manage: Should be enabled and populated with the username of the local account that will be controlled by Microsoft LAPS.
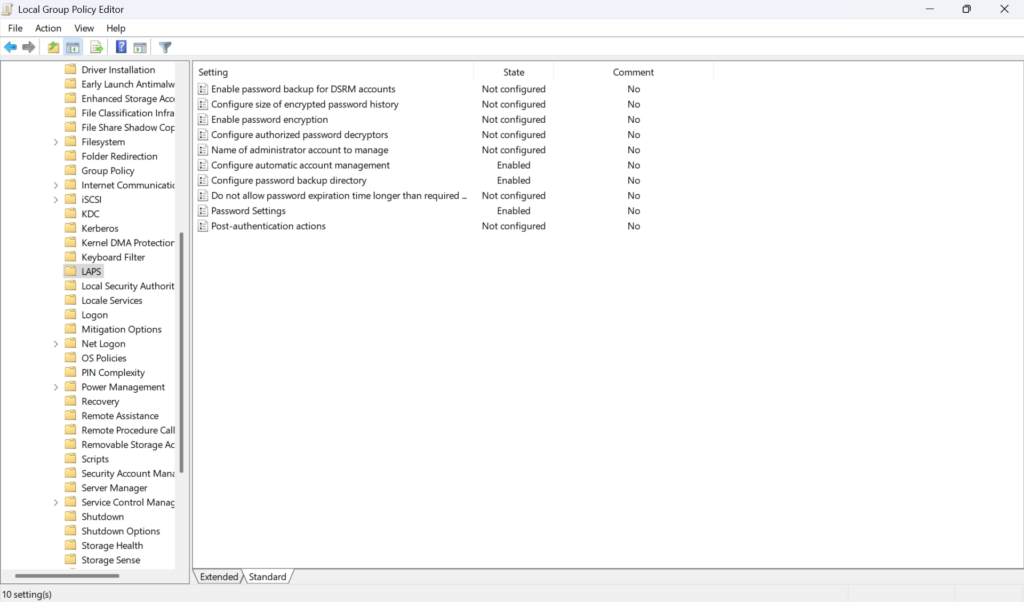
Additionally, you can set the Password Settings object to configure the complexity and length of passwords generated. This will help align with corporate security policy.
Once the group policy objects are set, update group policy on the local workstation by running gpupdate /force via Command Prompt. The prompt should return a successful message once complete. Return back to Entra ID and drill into the workstation by clicking on the workstation name. On the left side navigation, select Local administrator password recovery. If your group policy updates were successful, an option to Show local administrator password will display where you can view the password as well as the last and next password rotation timestamps.

At the expiration date, the password will rotate and the new password will be displayed in Entra ID. To test the rotation process, open Powershell on the workstation and run Reset-LapsPassword to trigger a password rotation. When refreshing Entra ID, the two timestamps for last rotation and expiration should be updated as well as a new password. This confirms that the backup to Entra ID is working correctly.
In addition to using local group policy, a registry hive can be imported to apply these same settings in mass. The registry values are stored in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\LAPS. A sample export is below:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\LAPS]
"BackupDirectory"=dword:00000001
"PasswordComplexity"=dword:00000004
"PasswordLength"=dword:0000000e
"PasswordAgeDays"=dword:0000001e
"PassphraseLength"=dword:00000006
"AutomaticAccountManagementEnabled"=dword:00000001
"AutomaticAccountManagementTarget"=dword:00000000
"AutomaticAccountManagementNameOrPrefix"="Administrator"
"AutomaticAccountManagementEnableAccount"=dword:00000001Windows LAPS paired with Microsoft Entra ID makes local admin user management a breeze, automating the compliance of password complexity and regular password rotations.
